If you want to display text in your app you can use the Text object.
You can use the
Other options you will see used in the samples include
Use the SetText and GetText functions of the Text object to set and get it's text.
Example - Single line
{
lay = app.CreateLayout( "Linear", "VCenter,FillXY" );
txt = app.CreateText( "Hello" );
txt.SetTextSize( 22 );
lay.AddChild( txt );
app.AddLayout( lay );
}
def OnStart():
lay = app.CreateLayout( "Linear", "VCenter,FillXY" )
txt = app.CreateText( "Hello" )
txt.SetTextSize( 22 )
lay.AddChild( txt )
app.AddLayout( lay )
You can change the look of a Text using the SetBackColor and SetTextColor functions on the Text object.
Example - Multi line
{
lay = app.CreateLayout( "Linear", "VCenter,FillXY" );
txt = app.CreateText( "Hello\nWorld", 0.8, 0.2, "Multiline" );
txt.SetTextSize( 12 );
txt.SetTextColor( "#ff6666ff" );
txt.SetBackColor( "#ffffffff" );
lay.AddChild( txt );
app.AddLayout( lay );
}
def OnStart():
lay = app.CreateLayout( "Linear", "VCenter,FillXY" )
txt = app.CreateText( "Hello\nWorld", 0.8, 0.2, "Multiline" )
txt.SetTextSize( 12 )
txt.SetTextColor( "#ff6666ff" )
txt.SetBackColor( "#ffffffff" )
lay.AddChild( txt )
app.AddLayout( lay )
Text can be shortened using ellipsis (...) when the size of the control is too small to show all the text. Use the SetEllipsize to control where the ellipsis is placed. Available modes are
Example - Ellipsize
{
lay = app.CreateLayout( "Linear", "VCenter,FillXY" );
txt = app.CreateText( "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog", 0.75 );
txt.SetTextSize( 28 );
txt.SetEllipsize( "end" );
lay.AddChild( txt );
app.AddLayout( lay );
}
def OnStart():
lay = app.CreateLayout( "Linear", "VCenter,FillXY" )
txt = app.CreateText( "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog", 0.75 )
txt.SetTextSize( 28 )
txt.SetEllipsize( "end" )
lay.AddChild( txt )
app.AddLayout( lay )
You can also set a background image/pattern or background gradient for the Text using the SetBackground and SetBackGradient functions. See Layouts for examples of how to use these functions.
Properties
The following properties are available on the Text object:
Methods
The following methods are available on the Text object:
hexadecimal:
colourName:
 ”
”Adjust the visual color effect of the control by setting the Hue (by angle in degrees in a color circle), the saturation, brightness and contrast of the control.
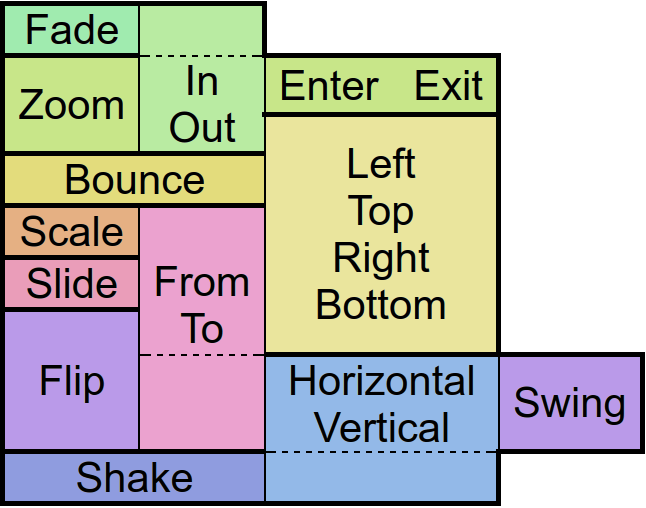
Animates the control.
There are
Batch method calls to be able to set all object's properties at once.
Note that you need to specify each parameter (use
Inherited methods can be called by appending an underscore to the function name (ie. txt.Batch({ SetBackColor_: [
Removes the focus of the control so that the user no longer has immediate access to it.
An object for saving individual extra properties.
Set the focus to the control so that the user can interact with it immediately.
Get the absolute height of the control in pixels.
Note that unlike the objects margins its padding does change this value.
Get the absolute width of the control in pixels.
Note that unlike the objects margins its padding does change this value.
Get the height of the control as screen height relative float or in pixels with the px option.
Note that unlike the objects margins its padding does change this value.
Returns the html formatted content.
Get the distance from the control to the left parent border as width relative float or in pixels with the px option.
Returns the amount of lines in the text even with html formatting
Returns at which character in the text a certain line begins.
Returns the top position of a given line on the screen.
Returns the maximum amount of lines the control can hold with the current control and font height
Returns the parent control object where the object was added to - commonly a layout.
Returns data about the position and size of the control.
If the screen option is given the position on the screen will be returned. Otherwise relative to the parent control.
The px options turns the relative values into pixels.
Returns the current displayed text of the control.
Returns the current size of the contained text. If the px option is given the size will be retured in pixels.
Get the distance from the control to the upper parent border as height relative float or in pixels with the px option.
Returns the control class name.
Returns the current visibility state of the control. The Values are:
Show: visible
Hide: invisible but still consuming space
Gone: invisible and not consuming space
Get the width of the control as screen width relative float or in pixels with the px option.
Note that unlike the objects margins its padding does change this value.
Hides the control without consuming any more layout space as if it were never there.
Hide the control but keep the layout space free.
Returns whether the control is currently useable by the user.
Returns whether the control overlaps with another by a given distance.
Returns whether the control is currently visible to the user, ignoring overlaying controls.
Append a string to the text separated with a line break
Allows access to other functions defined on the object in Java via reflection.
Resize a control after device rotation by keeping the original width/height ratios.
Set the transparency of the background by an alpha value between 0 (no transparency) and 0.99 (full transparent) or 1 (no transparency) and 256 (full transparent)
Changes the background color of the control.
Define the background color of the control with a gradient. The default gradient direction is from top to bottom, but you can change it from left to right and the reversed versions of course.
Define a radial color gradient for the background of control.
Changes the background to an image which can be repeated using the repeat option.
An image which is often used with that option is '/res/drawable/pattern_carbon' - try it out!
Adjust the visual color effect with a color and a given BlendMode. More information about BlendMode can be found in the Android Developer page.
Set a control description for accessibility
Will cause the inner text to be broken with ... at the start or the end if it cannot fit in the control.
En/Disable the control physically and visually so that the user can/can not access the control. Events like OnTouch will still be fired.
Change the font style by defining a font file.
Change the current text of the control to html-formatted text.
Define a maximum amount of log lines
Define a distance to other controls on each side of the control.
Define a callback function which is called when the object has been long pressed.
Define a callback function that is called when the user touches the control. In addition, an event object is passed to the callback function to obtain information about the touch type, the touch position(s), the amount of touches and the control that was touched.
Define a callback function which is called when the user started toching the control.
Define a callback function which is called when the user drags a finger over the screen.
Define a callback function which is called when the users finger leaves the screen.
Define distances that elements within the control are to maintain from the control borders.
Defines the position and size for the control if the parent is an absolute layout.
Scales the control along with its contents by the factors passed to the function.
Change the size of the control in either screen relative values or in pixels if the px option was given.
Change the currently displayed text in the control.
Change the text color of the contained text.
Define a shadow displayed around the control.
The sun is always shining so there has to be one. Always.
Change the size of the contained text.
En/Disables touch events to be fired on the control. Other events like OnChange will still be fired.
Change the visibility of the control to one of the available modes:
Show: visible
Hide: invisible but still consuming space
Gone: invisible and not consuming space
Set the visibility of the control to
Performs an animation on the control.
The target object is for the position, size and rotation that the control has at the end of the animation.
The type specifies the behavior and the speed of the animation. Separated by a dot, you must also specify whether you want to apply this behavior to the beginning (In), end (Out), or to both (InOut) times of the animation.
With the amount of repeats you can control how many times you want to play the animation.
If you have jojo activated, the animation will alternate between forward and backward playback, so that if the repetition value is odd, the control will be at the start position again at the end of the animation.
Finally the callback function will be called after the animation has finished. Well, it's about time!